What changes with the transition to the new DVB T2 standard for digital terrestrial. Differences from the first generation, the real times for the switch off, compatible televisions and devices. When buying a new TV.
We started talking about DVB T2 technology in 2017: it is an improved version of the DVB-T standard that DVB ( Digital Video Broadcasting ), a European consortium that defines shared modes for digital terrestrial television broadcasting, began to propose. Already in 2006.
A historic step was recorded in 2012 when analog TV finally migrated to digital terrestrial in its first version known as DVB-T (“T” stands for terrestrial ).
Between 21 and 30 June 2022, a new switch off will occur after about ten years, this time with the definitive transition from DVB-T to DVB T2, the new digital terrestrial.
The reasons for the transition from DVB-T to DVB T2 in brief and the regulatory indications
With DVB T2, the goal is to improve reception using fixed and portable devices, increasing the bitrate simultaneously.
DVB T2 uses error correction codes similar to those used with the DVB S2 satellite standard, allows the use of MIMO systems, well known in the WiFi field, provides methods to reduce the peak power radiated to the transmitting antenna, allows users more than 8,000 carriers, estimate the best channel using fewer pilot carriers, use different versions of coding and modulations, increase the distances between antennas and receivers, encapsulate IP packets in the stream, and more.
Stakeholders agreed on a roadmap for the switch to DVB T2, as reported on this page and as established in the relevant ministerial provision.
Let’s try to summarize the “fixed points” regarding second-generation digital terrestrial (DVB T2), clarify the timing of the transition, and the cases in which it is necessary to buy a new TV.

DVB T2: the important dates to know
Let’s start with a premise: the 2018 Budget Law on ” Efficient use of spectrum and transition to 5G technology ” has already set a “watershed date,” namely July 1, 2022. In reality, as we will see later, the switch-off has been slightly anticipated to 21-30 June 2022.
By that date, television networks will have to adapt to the reorganization of frequencies on the 700 MHz band to be fully available for mobile networks that offer 5G connectivity.
In Italy, the various telecommunications operators have been licensed to use the frequency bands on 694-790 MHz, 3600-3800 MHz, and 26.5-27.5 GHz to provide fifth-generation connectivity services.
Starting from September 1, 2021, and until June 20, 2022, the shifting of the television networks’ frequencies will begin, which will gradually abandon the 700 MHz bands.
The first regions where it will start (operations must be completed by 31 December 2021) are Lombardy, Piedmont, the province of Trento, the province of Bolzano, Valle d’Aosta, Veneto, Friuli Venezia Giulia, and Emilia Romagna.
On 1 January 2022 (until 31 March 2022), it will be the turn of Campania, Lazio, Liguria, Tuscany, Sardinia and Umbria; from 1 April 2022 until 20 June 2022, the transition will finally take place in Sicily, Calabria, Puglia, Basilicata, Abruzzo, Molise, and Marche.
On September 1, 2021, it is also set the national passage of all broadcasts in MPEG4 AVC (H.264), albeit still using the current DVB-T standard.
This is an intermediate step that will help in making the best use of the available band following the passage of some frequencies to the provision of 5G services.
From September 1, 2021, to 21-30 June 2022, those who are already able to receive HD channels from 501 onwards will still have no reception problems precisely because their devices can correctly manage the MPEG4 standard.
Finally, as mentioned, between June 21 and June 30, 2022, television operators are called upon to embrace the DVB T2 standard and HEVC coding. (see below for the meaning of HEVC).
From this point on, those who use TVs and devices that are not compatible with DVB T2 HEVC but only DVB-T MPEG4 will no longer receive the signal because the switch off will be simultaneous with the activation of the new transmission mode.
After 21-30 June 2022, non-DVB T2 HEVC compatible television signal receiving devices (digital terrestrial) will no longer receive programs from any national network.
When do you need to buy a new TV or set-top box? How to tell if the TV is compatible with DVB T2?
From January 1, 2017, the various sales channels are authorized to market exclusively devices equipped with a DVB T2 HEVC tuner.
Those who bought a new TV from the beginning of 2017 onwards can already be sufficiently sure that they are ready for the switch off in mid-2022. However, it is necessary to pay particular attention to some specific technical aspects (see below).
HEVC (High-Efficiency Video Coding ), also known as H.265, is a video compression standard that goes hand in hand with DVB T2. HEVC is the heir to H.264 / MPEG-4 AVC: it improves video quality, doubles the data compression ratio compared to H.264, and supports 8K ultra definition going up to 8192 x 4320 pixels. In the article HEVC or H.265: main differences compared to H.264. Given AV1, we have put the main features of HEVC under the lens.
The TVs placed on the market from January 1, 2017, as mentioned, are HEVC compatible.
Some mid-range TVs purchased in 2015-2016 should also be DVB T2 HEVC compatible.
- A few useful observations on TVs and devices purchased before 2017
For televisions before 2017, the suggestion is to note the exact model and then carry out a search online, preferably on the manufacturer’s website, for the complete technical specifications.
In this way, it will be possible to verify the possible compatibility with DVB T2 HEVC 10 bit.
The data on color depth (10 bits) is fundamental because devices compatible only with 8-bit DVB T2 HEVC will not allow digital terrestrial channels after the switch off in mid-2022.
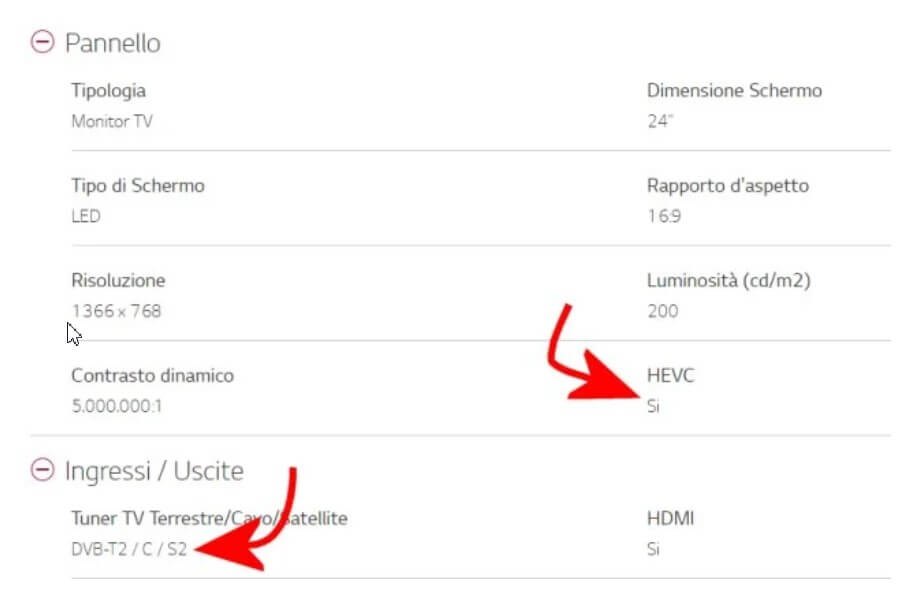
TVs dating back to the years 2014-2015 integrate DVB T2 support but not the HEVC codec. This limitation will make it impossible to receive the new channels after the switch-off of 21-30 June 2022: it will be necessary to equip yourself with an external decoder (they cost a few euro) or change TV.
It is unlikely, if not impossible, to release firmware updates capable of activating compatibility with the HEVC codec: it is, however, worth trying to consult the manufacturer’s Download area after searching for the exact TV model by entering the corresponding code.
A firmware update can always change the TV’s software’s behavior but cannot change the hardware configuration of the chip used for video decoding.
If the decoder chip had enough hardware to support HEVC, the manufacturer could release a firmware update. Otherwise, this will never happen.
How to check the compatibility with DVB T2 of your TV and the integrated digital tuner?
From mid-January 2020, two channels (100 and 200 of digital terrestrial) are active, managed respectively by Rai and Mediaset, which allow you to check your TV’s compatibility with DVB T2 HEVC.
In addition to “sifting” through the specifications, it is sufficient to re-tune the digital terrestrial and then go to channels 100 and 200.
The appearance of a “sign” similar to the one shown in the figure (transmitted with 720p resolution) confirms that the device, at the moment of the definitive switch off (see point 10 below), it will be able to receive DVB T2 HEVC broadcasts without adopting accessory devices (i.e., compatible decoder).

If the TV currently in use is unable to tune both channels 100 and 200, if the screen is completely black or messages are displayed about the channels’ unavailability, it means that the TV is not compatible with DVB T2 HEVC 10 bit.
On TV with 8-bit HEVC support, you will see a black screen after the switch off.
As mentioned above, 10 bits refer to the color depth that can be managed with HEVC or 1 billion colors.
It must be said that at the local level, depending on the area of residence, channels 100 and 200 could still be occupied by other broadcasters. In the tuning phase, resolve the conflict by possibly opting for the test “cartel.”
The presence of the DGTVi PLATINUM sticker confirms that the TV or decoder is fully DVB T2 and HEVC compatible. There are several versions of the “sticker,” but the PLATINUM one offers, at a glance, the maximum guarantee (more information at this address.
A new decoder to receive DVB T2 HEVC channels after the end of June 2022
On Amazon, there are already many DVB T2 HEVC decoders ready for use at the maximum price of about 35 euros: just connect them to the TV via HDMI port or with the very old SCART socket if you have an even older TV (and you don’t still want to deliver it as WEEE waste in specialized collection centers).
From now to mid-2022, keep an eye on the market because Android TV boxes will certainly be released equipped with antenna connectors for receiving digital terrestrial and satellite signals compatible with the various technologies and integrate DVB T2 HEVC digital tuner.
The advantage will be to be able to have devices that will not act as simple “basic” decoders but will combine these technical characteristics with the possibility of installing Android applications of all kinds.
Starting from December 2019, interested citizens can access the TV bonus for replacing old televisions and appliances and purchase DVB T2 compatible decoders or televisions.
The state incentive has a maximum value of 50 euros and is aimed at citizens with an ISEE income bracket not exceeding 20,000 euros. To benefit from it, just fill in the form and deliver it to the seller together with an identity document and tax code.
What are the main alternatives to DVB T2?
The alternative to DVB T2 obviously exists and is called a satellite. This platform uses the DVB-S2 HEVC standard. The channels that can be used via digital terrestrial (except some minor broadcasters) are accessible through the well-known free platform tivùsat.
However, it is necessary to equip yourself with a compatible satellite decoder or a CAM to be inserted in the TVs that allow it to be hosted (it must be certified) and a special smartcard (see here for more information ).
On tivùsat, there are 50 channels in high definition and 5 in 4K UHD, but trivial to say, CAM and 4K smartcard will not be fully exploitable if the TV stops at Full HD 1080p as a supported resolution.
A tech-savvy writer with a knack for finding the latest technology in the market, this is what describes John Carter. With more than 8 years of experience as a journalist, John graduated as an engineer and ventured soon into the world of online journalism. His interest includes gadget reviews, decoding OS errors, hunting information on the latest technology, and so on.


















