
We are going to explain to you what exactly the CPU of a computer is and what it is for. It is a tremendously complex component. However, it is the brain of each computer or device, but we are going to try to explain everything in as simple a way as possible so that you can understand the basic concepts of its operation.
Much more could be said about a CPU than what we are going to tell you since it is possible to delve much deeper into the characteristics of its operation. However, what we want here is that if you have never heard of it, you can understand its fundamentals so that you at least know exactly what we are talking about.
What is CPU
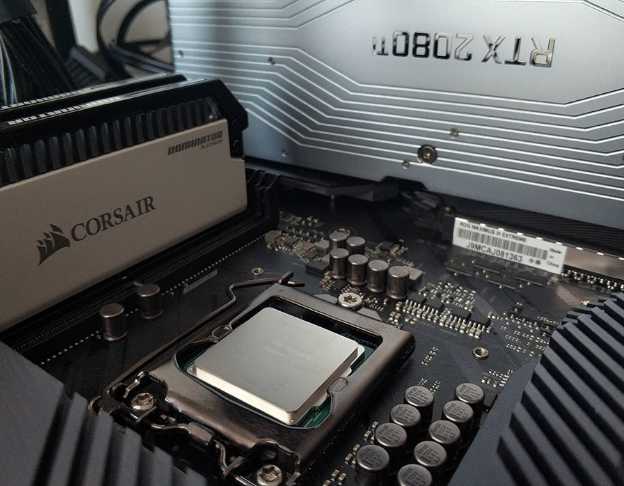

CPU stands for Central Processing Unit, which translates means Central Processing Unit. It is one of the vital components that you will find in your computer, your smartphone or your tablet, or your laptop, and even in watches and practically any electronic device. Without it, they simply couldn’t function.
The CPU is often referred to colloquially as a microprocessor or simply a processor, and you can think of it as the brain of any device. It is in charge of processing all the instructions of the device, reading the orders and requirements of the operating system, as well as the instructions for each of the components and applications.
So, just like the brain, the CPU is in charge of ensuring that everything works correctly and of interpreting everything that the operating system or the components want to do, establishing the connections, and performing all the necessary calculations for it to work. The more powerful the processor, the faster it can do operations and the faster your device will run overall.
It is also in charge of reading, interpreting, and processing the instructions first of the operating system and then of the programs or applications that you have installed on your computer. When you open Word or your browser, it has to load, and for this, you need to carry out a series of steps whose instructions are sent to the processor. Each action that you then do inside will also send instructions to be able to be executed and carried out.
Your computer or laptop will have a dedicated CPU to carry out all the operations and processes that the system requires. Meanwhile, mobiles have the so-called SoC or System on Chip, which is a chip that contains both the CPU and other components, such as integrated graphics chips. With this, SoCs can often do more than the functions of standard CPUs.
How is the CPU
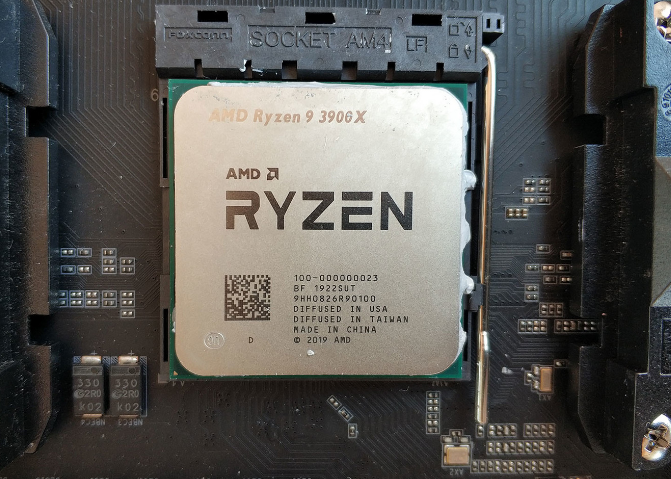

The CPU is usually small, square in shape, and has metal connectors and pins. In general, it is usually installed on the motherboard of a computer in a special socket that can be in different places depending on the motherboard. The processor is not soldered to the board, so you can change the CPU of one computer for another if you want.
The CPU has a minimum of a processor or Core inside, a chip to perform calculations and operations. At first, they all had only one, but over time CPUs have increased the number of these cores, and there are different ways to call them depending on this number.
For example, if you’ve ever heard that a processor is Dual-Core or dual-core, it’s because it has two of these chips inside. Then they evolved to four, the Quad-Core, and have been increasing with six, eight, or even 12 cores or more. All of them are identified by that name that includes the word Core, but before that, a reference to the number of cores is placed.
The fact that the CPU has several processors or cores usually means that it is capable of performing more operations at the same time, so it can perform faster and better. However, this does not always mean that the more cores there are, the faster everything will be since this is something that also depends on how each of the cores are.
For example, some processors from Intel and AMD, the two main manufacturers, have technologies that allow them to execute two execution threads in a single core, which are the instruction sequences belonging to the operating system or application. The execution threads, or threads in English, are the sequences of instructions belonging to the operating system or an application.
What does this mean? Well, in processors that have this technology, each physical Core can act as if it were two virtual cores since each one can work with two different threads or sequences of instructions.
And then, there is the frequency of the processor, which is marked in gigahertz. The frequency, also called the clock, is what sets the pace with which the processor works. A hertz is an action that is repeated once per second, thus increasing up to the Gigahertz, which is 1,000,000,000 actions per second.
The work rate of a processor is marked by the ability to perform as many actions per second as possible since each operation of an application can require several clock cycles or actions.
In short, it is not only the number of processors that matters but how each one works. The more GHz, a processor, has, the faster it will be. This, in the most simplified terms, means that if you have a 1GHz quad-core processor, it will be slower than a 2.5GHz dual-core processor.
What is the CPU for?

Your computer’s CPU is what executes a sequence of instructions and processes the data from them. These sequences of instructions are those carried out by the programs that you have installed on your computer. Come on; they are in charge of carrying out the operations that the programs or applications need to carry out the tasks that you ask them to do.
You tell your photo app to apply a calculation. This application gives the computer instructions with the calculations or actions it needs to perform to carry out the task. The instructions are put into RAM, where they are picked up by the CPU, which is what carries them out.
To do this, several different steps are followed. The first is to read the data and instructions to perform each of the application tasks. The data is decoded and partitioned so that it can be understood by the different parts of the CPU, which execute the actions, perform the calculations, and write the results to the main memory, either as a result or for later use in other operations.
But this is an extreme simplification since these basic functions of the processor are performed per instruction, and each program may require several instructions to act. In addition, these are not performed in order, and one after the other, but the processor can be working with many functions at the same time for the different active programs.
You have to understand that everything on your computer is represented by numbers, so the CPU is in charge of collecting and calculating the operations of these numbers. With these operations, exactly everything you do on your computer is done, from opening the Windows start menu to watching a video on YouTube; everything requires a series of instructions and calculations to be able to be carried out.
In modern computers, the CPU is not the one that does everything since other specialized components usually interfere, such as the graphics card for everything related to what you see on the screen. RAM also comes into play to store fast-access data and the rest of the components inside your computer.
In this swarm of devices and components, the CPU is the brain or the conductor since it is the one that organizes everything so that the tasks are done where and in the way they should be done to obtain the desired results.
The CPU is not more essential than other basic components of a computer since it will not work without a power supply or other components. Nor is it whole on which the execution of tasks depends, since for everything related to the production of videos or the visualization of video games, it is also necessary to have a good graphics card or GPU and good RAM.
But the speed and power of the CPU can depend on how fast a computer goes, and having a good or bad CPU will affect the performance of your computer.
Sharlene Meriel is an avid gamer with a knack for technology. He has been writing about the latest technologies for the past 5 years. His contribution in technology journalism has been noteworthy. He is also a day trader with interest in the Forex market.











