NFC is a short-range communication technology that finds its most common application in the field of electronic payments. What is NFC, how it works, and what are the other possible uses?
Until recently, only top-of-the-range smartphones integrated an NFC chip. However, now, it is possible to find it integrated even in medium-high-end mobile devices. But what is NFC, and what is it for?
NFC, an acronym for near-field communication, is a technology that provides short-range (10cm) wireless connectivity that has been jointly developed by Philips, LG, Sony, Samsung, and Nokia.
If it is about proximity communication, as in Bluetooth, to arrive with a lower coverage range, what advantages does NFC bring with it?
Let’s start by saying that NFC does not come from anything but is the evolution of the well-known contactless identification and communication technology, RFID. The latter was used mainly in the industrial field as an electronic label, to provide information on objects and animals. But while RFID works “one way,” NFC allows you to establish a two-way data exchange. This is true for NFC Android, NFC iOS, or NFC Windows platforms.
Therefore, through NFC, it is possible to quickly synchronize data between two devices, even if they are completely different from each other (a peer to peer network is established ).
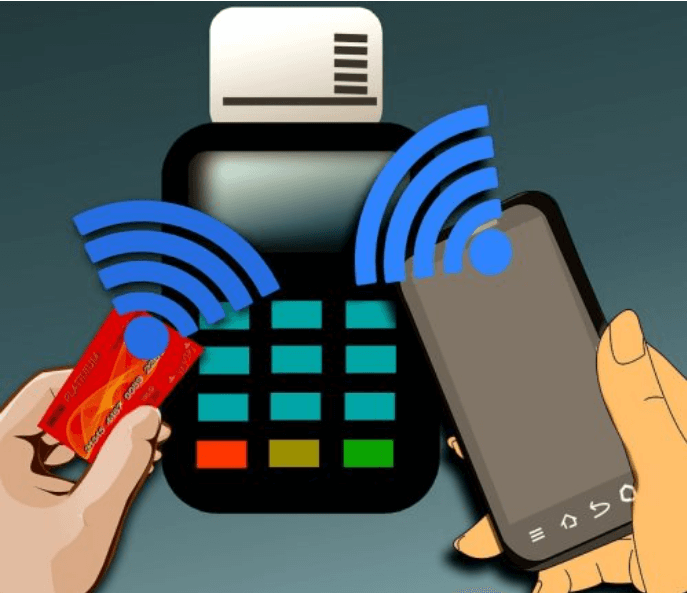
Using your NFC compatible mobile device, you can easily manage contactless payments. The smartphone turns into a sort of electric purse and – after installing a particular app – you can make a transaction only by bringing the phone close to the POS of the merchant. This is similar to how the Miracast functions.

Payments via NFC devices are becoming more and more popular also thanks to the launch of services in Italy such as Google Pay, Apple Pay and Samsung Pay. The app installed on the mobile device that supervises payments made via NFC can be combined with different payment methods: credit cards, debit cards, and in some cases, even PayPal (as it allows, for example, to send payments via Google Pay). In this way, payment can be made by bringing your device closer to the POS, the vending machine, the cash register, without ever extracting wallets and cards, and without the retailer or the banking system being able to know the data of their credit cards or PayPal accounts used.
A notebook equipped with an NFC chip can enable contactless payments in the same way.

NFC versus Bluetooth
Many wonders why NFC exists when Bluetooth technology has already existed for some time.
Many reasons justify NFC’s birth, which demonstrates that Bluetooth is not the best choice in some application fields.
With Bluetooth, it is essential that the devices already have active communication; they must be previously paired with each other and necessarily be powered. This brings in additional requirements that complicate things when it is essential to establish a fast and secure exchange of data.
NFC also requires the two devices to be physically positioned at a very short distance. In this way, it is possible to significantly reduce energy consumption and ensure that data is transmitted to and from a device located in the immediate vicinity. Think of the case of electronic payments: with NFC, the paying user’s smartphone must be in front of the POS; otherwise, the transaction and the consequent charge will not be successful. For safety reasons, the distance at which the two devices must be found is usually reduced to less than 4 centimetres.
This is why NFC is also perfect when you want to opt for cerca numero cellular for quick data transfer.
Bluetooth transmits data on the 2.4 GHz band, which is, as you know, now very crowded: think of WiFi, cordless phones, baby monitors, and many other electronic devices.
To avoid any communication problems, NFC uses a much less crowded area of the spectrum (13.56 MHz) and takes some technical measures to prevent any adverse effects caused by any interference.
How to check if your smartphone supports NFC
The best way to check if your smartphone has an integrated NFC chip is to check its specifications.
You need to access the operating system settings and type NFC in the top’s search box on Android devices.
Usually, however, NFC references are found in the Wireless and networks or Network and Internet sections.
To activate the NFC chip, tap the corresponding option: ” Allow data exchange when the phone touches another device. “
What NFC technology is for
As we mentioned earlier, NFC certainly does not offer Bluetooth’s performance – much less that of WiFi – during data exchange: it can send and receive information with a maximum transmission speed of 424 kbps.
Therefore, it is perfect for making payments with your smartphone because the amount of data exchanged is minimal.
The use of NFC chips is gaining ground on U2F FIDO2 tokens: they allow you to use a key as a tool to securely authenticate to major online services.
Although there are also FIDO2 Bluetooth keys, the trend is to focus exclusively on the use of USB and NFC.
Yubico, a leading company in the design, production, and marketing of U2F FIDO2 keys, has repeatedly argued that products based on the use of Bluetooth technology do not offer sufficient guarantees in terms of safety. Yubico had initially evaluated the possibility of placing Bluetooth (BLE) keys on the market, preferring to refrain from doing so for reasons of safety, usability, and durability.
The company then criticized Google and its Titan Key, which, while integrating an NFC chip, for the moment, only uses Bluetooth.
Yubico does not claim that NFC is inherently safer than Bluetooth. Since both NFC and Bluetooth communications can be monitored and “spied“, a first reassurance comes from the very small coverage range of NFC (a few centimeters) and the contained RF powers involved.
As is well explained in this study, it is then the use of applications that adopt cryptography and adequate security measures to offer the best guarantees.
NFC chips are also increasingly used on multimedia devices: think of an NFC compatible Bluetooth speaker. In this case, the data transfer (therefore, the music tracks) takes place via Bluetooth, but the actual connection procedure can be carried out via NFC.
Thus the connection between speaker and smartphone will instantly occur without having to intervene on the Bluetooth configuration manually.
However, NFC can also be used to exchange files between devices, but the data transfer speed will not be convincing.
In Android’s case, to use NFC to transfer files between smartphones and other compatible devices, activate Android Beam: data exchange will take place instantly by merely touching the two devices.
More information in this support document.
Finally, there are small devices, called NFC tags, inspired by the “RFID philosophy.” For example, it allows you to send useful information such as web addresses, telephone numbers, GPS positions, identification data to a smartphone, or automate certain operations.
Some NFC tags are available on Amazon at a very affordable price, can be programmed to allow quick logins on the main online services, to activate or deactivate WiFi and Bluetooth on the phone, to send reminders or enter events in the calendar, to make phone calls or send SMS (they can therefore also be configured as tools to send requests for help instantly). It can also be programmed to deliver functions such as “business cards,” as part of promotional initiatives to offer coupons and vouchers, to adjust volumes and lighting levels, to activate Bluetooth in the car, and much more.
A tech-savvy writer with a knack for finding the latest technology in the market, this is what describes John Carter. With more than 8 years of experience as a journalist, John graduated as an engineer and ventured soon into the world of online journalism. His interest includes gadget reviews, decoding OS errors, hunting information on the latest technology, and so on.











