Where is the Startup folder in Windows 10, and how to use it? What are the alternatives in the latest version of the Microsoft operating system and the previous ones to automatically start applications and scripts?
Windows 10 users often wonder where the “historic” Startup folder went that in Windows 7. In previous versions of the Microsoft operating system, it always appeared in the Start menu. It has not disappeared, and today as in the past, it allows you to start specific applications after entering the selected user account.
You can find items added after installing some programs in the Startup folder, but you can also insert links and executables.
In Windows 10, the Startup folder and its contents are stored, at the file system level, in the % appdata% \ Microsoft \ Windows \ Start Menu \ Programs \ Startup path.
To quickly open the folder and check what it contains, you can simply press the Windows + R key combination, then type shell: startup and press Enter (it also works with previous versions of Windows, not just in Windows 10).
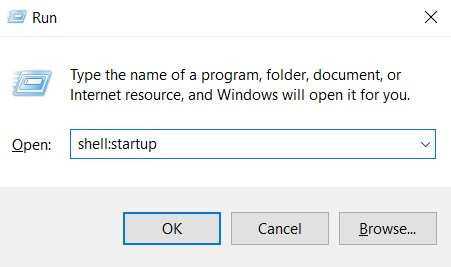
As was the case in previous Windows versions, programs can run automatically at startup using other methods: to discover them all, just download and start the Autoruns utility.
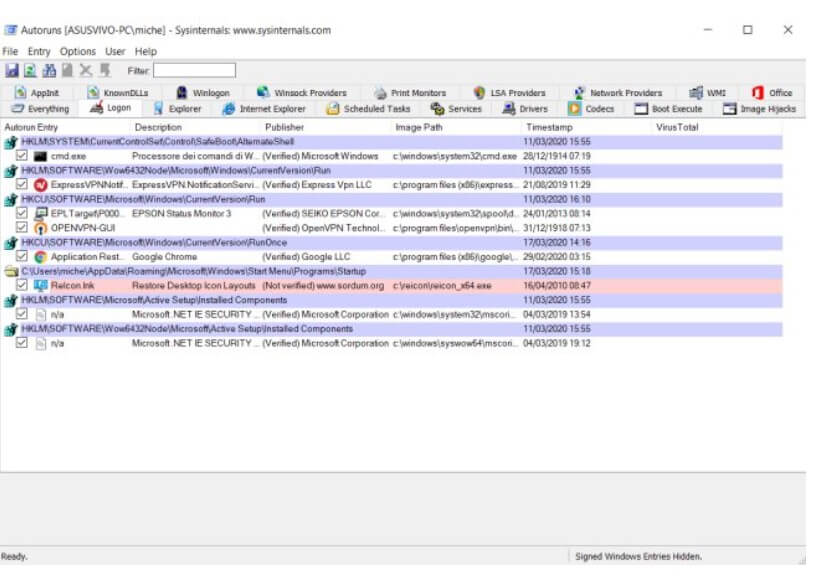
By clicking on the Logon tab, you will get the list of programs loaded automatically using standard locations offered by Windows. In the section … \ Roaming \ Microsoft \ Windows \ Start Menu \ Programs \ Startup, you will get the applications configured to run automatically from the Startup folder, as seen above.
However, as you can see, there are other areas of the system and locations of the Windows registry: Regedit and system registry: guide to the most useful aspects.
By clicking on the AppInit, Winlogon, Image Hijacks, and Boot Execute tabs, you can check if some programs on your system were using less common gimmicks to run automatically. Finally,
the Scheduled Tasks tab collects the list of applications and scripts that are started programmatically using the Windows Scheduler (see below).
In all cards, the elements highlighted in pink are those “no” ( not verified ) or files that have no digital signature (Autoruns has not been able to verify the identity of the second developer).
How to add an autorun program
To make sure that every time Windows starts, or rather after logging in with the user account currently in use, a program is automatically run, simply press the key combination Windows + R, type shell: startup, right-click in a free area of the window then select New, Link from the context menu.
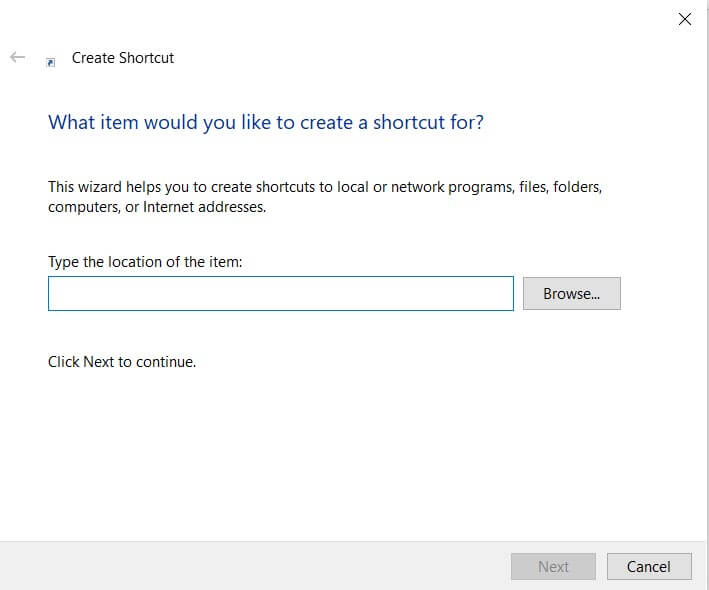
In the field Enter the path for the connection, using the Browse button if necessary, you can indicate the file or script to be started, specifying – where necessary – the necessary options. In this way, it is possible to automatically start a program that requires the use of some switches when entering Windows. Consider, for example, starting a backup task using Robocopy : Robocopy: how to quickly copy files and folders on the local network.
Automatically run with Windows Scheduler
Alternatively, you can use the Windows built-in Task Scheduler (press Windows + R then type taskschd.msc ) and click Create Task in the right column.
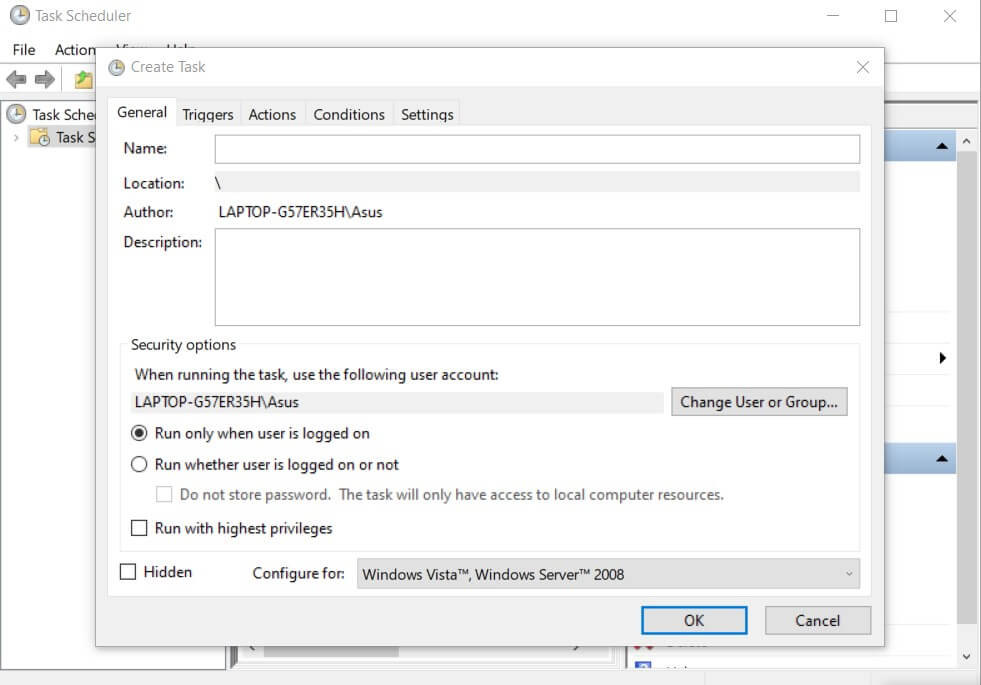
The advantage of using the Scheduler is that you can set the execution of tasks periodically even when the current user is not “logged in” on the system (does not have an active session; option Run regardless of the connection of the users ) and request the use of administrator privileges if necessary ( Run with highest privileges box ).
Using the Activation tab, you can decide when to start the activity: not only based on a schedule but also based on switching on or off the PC, system lockout, or closing the work session, in case of inactivity, and so on.
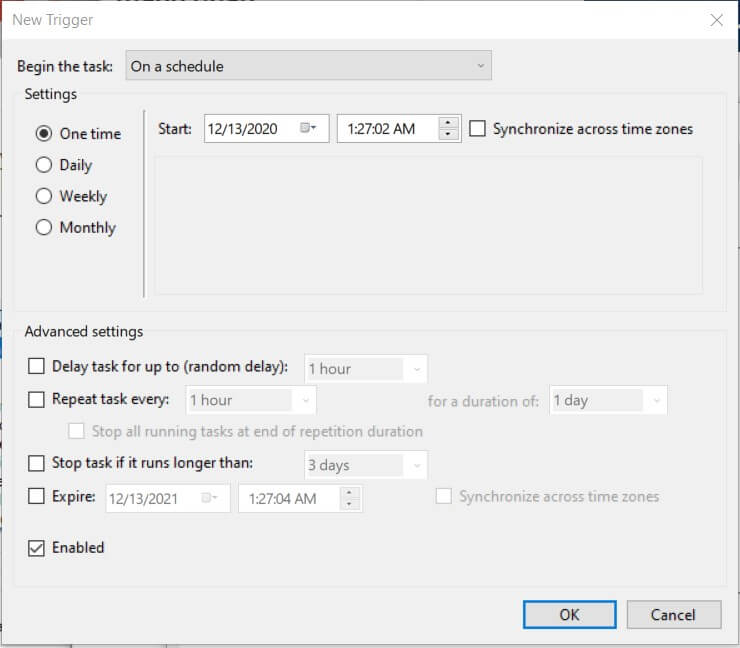
By clicking on Actions, New, you can set the program, programs, or scripts to be started. Unlike in creating a link, the Task Scheduler asks you to specify any arguments / options in the box provided.
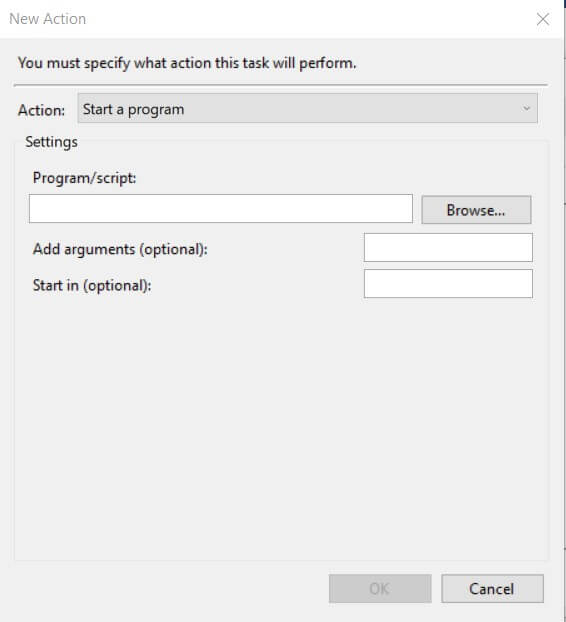
One aspect should be kept in mind to avoid unnecessary “headaches”: in the General tab, after activating the Run with the highest privileges box and correctly choosing an account with administrator privileges, while entering the corresponding password, you will get the message Error message ” Task-related error. Error message: The specified account name is invalid “.
This is an anomaly that Microsoft has not yet corrected: to overcome the problem. It is necessary to indicate MACHINE NAME \ ACCOUNT NAME in the Username field instead of just the user account name proposed by Task Scheduler.
Automatic execution with registry Run keys
The automatic execution of a system startup program can also be arranged using the system registry, as we have seen in the opening talking about the Autoruns utility.
By opening the Registry Editor and going to the HKLM \ SOFTWARE \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Run and HKCU \ SOFTWARE \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Run keys, you can make an application or script are automatically loaded for anyone who logs in to Windows (HKLM, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE) or for the user you are using (HKCU, HKEY_CURRENT_USER).
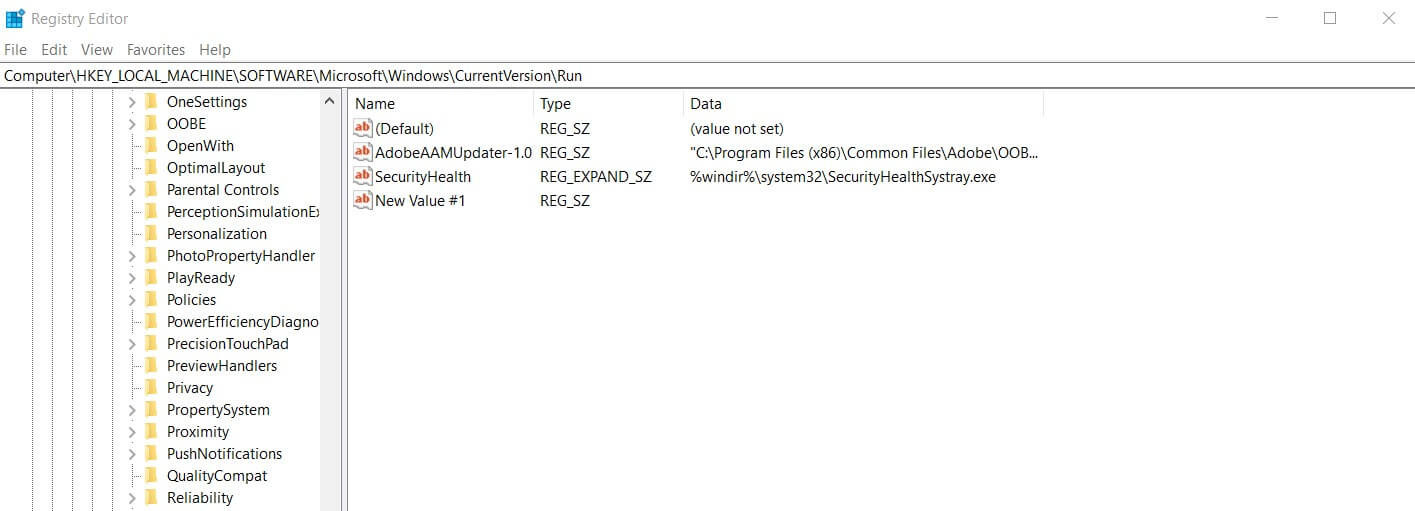
It is sufficient to create a new string value in the right panel by assigning it an arbitrary name and, in the Value data field, specify the application or script to run together with its arguments (if necessary).
Advice? Never forget to put the file’s path to be executed in double quotes.
Other registry keys that can be used to have automatic execution at Windows startup :
HKLM \ System \ CurrentControlSet \ Services
HKLM \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Explorer \ ShellServiceObjects
HKLM \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ RunServicesOnce
HKLM \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ RunOnce
HKLM \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Policies \ Explorer \ Run
HKLM \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \
HKLM \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ ShellServiceObjectDelayLoad
HKLM \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Explorer \ SharedTaskSchedulerHKLM \ Software \ Microsoft Active Setup \ Installed Components
HKLM \ Software \ WOW6432Node \ Microsoft \ Active Setup \ Installed Components
HKLM \ Software \ Microsoft Windows NT \ CurrentVersion \ Drivers32
HKCU \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ RunOnce
HKCU \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Run
HKCU \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Policies \ Explorer \ Run
HKCU \ Software \ Microsoft Windows NT \ CurrentVersion \ Windows \ load
HKCU \ Software \ WOW6432Node \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Run
HKCU \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ RunServices
HKCU \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ RunServicesOnce
HKCU \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ RunOnceEx
To check what happens on your system, the suggestion is always to use the Autoruns utility, which can examine the contents of all the various registry keys.
A tech-savvy writer with a knack for finding the latest technology in the market, this is what describes John Carter. With more than 8 years of experience as a journalist, John graduated as an engineer and ventured soon into the world of online journalism. His interest includes gadget reviews, decoding OS errors, hunting information on the latest technology, and so on.













