GPT ( GUID Partition Table ) is a standard for defining the partition table of a hard disk, which represents the evolution of the well known MBR ( Master Boot Record ).
GPT offers a more flexible mechanism for disk partitioning than the traditional MBR, brings with it several advantages, and is part of the EFI ( Extensible Firmware Interface ) standard whose purpose is to replace the “old” BIOS.
On newer systems equipped with UEFI ( Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), “interface” placed between the firmware and the operating system, and a substitute for the traditional BIOS, it is increasingly common to find hard disks that use GPT partitions. But what are the differences between MBR and GPT?
First of all, both MBR and GPT allow the operating system or operating systems installed to obtain precise information about the disk structure. Although MBR and GPT differ in their intrinsic architecture, they are two elements that play the same indispensable and fundamental role.
The MBR, boot sector present on the hard disk that contains information of crucial importance for the correct loading of the operating system occupies the first 512 bytes of the hard disk. It preserves the partition table, used by the system – among other things – for determining which partition is set as “active”. When, for various reasons, the information in the MBR is damaged or modified inappropriately, the risk is that of not being able to boot normally the system or systems installed on the hard disk.
Still widely used today, the MBR was born in the early 1980s, which is practically prehistoric in the IT field. Despite its longevity, MBR brings with it some limitations and some disadvantages. First of all, an MBR-based disk cannot host more than four primary partitions. To create more partitions, you can set the fourth partition as an extended partition and then insert more logical sub-partitions into it. Furthermore, each partition cannot exceed the maximum size of 2 Terabytes.
The MBR sector is the only memory location where all the information on the hard disk structure is stored. If its contents were to be damaged, it would be impossible to start the installed operating systems.
In the same article, we have also indicated some software that allows you to create a backup copy of the MBR, which can be easily restored in case of need.
GPT is an integral part of the UEFI standard (although it is also used in some BIOS to overcome the limit of 2 Terabytes per partition). It uses “global identifiers” (GUIDs) to refer to each partition’s contents on the disk.
Using GPT can create a theoretically unlimited number of partitions even if most operating systems reduce the number to 128.
However, this is not the only difference between GPT and MBR. While MBR limits the size of each partition to 2 Terabytes, GPT allows you to even reach up to 9.44 Zettabytes or over 9 billion Terabytes.
Microsoft Windows, however, reduces the maximum size of GPT partitions to 256 Terabytes.
From a structural point of view, GPT retains information about disk organization at the beginning of the hard disk and drive. This is an important feature (redundancy) that allows you to restore the correct loading of operating systems if the data stored in the initial header block should be damaged for any reason.
A series of checks on the integrity of the header GPT header ( CRC32 checksum ) allows immediate detection of any errors in the header and/or in the partition table.
As shown in this diagram, GPT also uses – as the first sector of the hard disk – a “protective” MBR. It has an important role in allowing a traditional BIOS to boot one of the operating systems installed on the hard disk using the special boot loader contained in the unit’s initial sector. The MBR at the head of the disk also helps protect its contents from the action of outdated utilities, which are unable to recognize and support GPT disks.
Which operating systems support GPT?
In the case of Windows, only 64-bit versions of the operating system can be booted from GPT partitions. Buying a personal computer or a notebook with Windows 8 or Windows 8.1 64-bit makes it highly likely that GPT partitions will be used.
On Windows 7, however, the default configuration always requires the use of the MBR instead of GPT.
On Apple Mac systems based on the Intel platform, GPT is used by default, and it will not be possible to install Mac OS X (unless special gimmicks are employed) on an MBR hard drive. Mac OS X, however, works on MBR drives: it is an only system installation, which by default, is not allowed.
With the most recent versions of the various Linux distributions, however, there is no problem: the penguin will install and run on both MBR and GPT partitions.
MBR or GPT? How to check if the disk uses one or the other scheme
To check, in Windows, if you are using MBR or GPT, you can open the command prompt with administrator rights, then start the diskpart utility.
Typing the command list disk, you will get the complete list of connected hard drives.
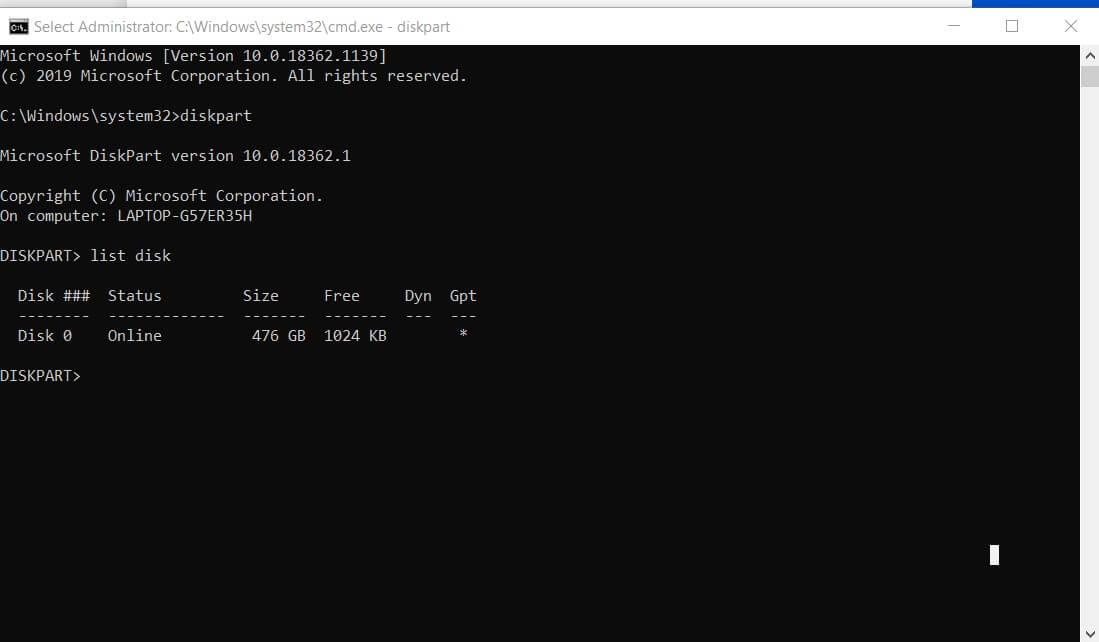
The GPT column contains the information you are looking for. An asterisk, placed next to the various units, indicates that the GPT standard is being used. Conversely, the absence of the asterisk reveals that the corresponding disk is using MBR.
To convert a disk using MBR to GPT (or vice versa), it is possible to use free software such as AOMEI Partition Assistant. Before proceeding, however, it is essential to make a complete backup of the disk contents, which can be restored in problems.
From the main screen of Partition Assistant, by clicking the right mouse button on a disk, you can choose to convert to GPT or MBR.
After confirming the operation, you will have to click on the Apply button to start the intervention.
AOMEI Partition Assistant Home
Download: aomeisoftware.com
Compatible with: Windows 2000, XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8
License: Freeware (allowed for both home and commercial use)
– All information on supported features is posted on this page.
– This page highlighted the differences between the free (Standard) and paid versions.

Taylor is a freelance SEO copywriter and blogger. His areas of expertise include technology, pop culture, and marketing.