We are going to explain to you what are the differences between HDD and SSD hard drives. For that, we are going to start by describing to you simply and easily understand what are the general features of hard drives, both mechanical or HDD, and solid-state drives or SSD. Thus, you can learn to recognize and differentiate them without problems.
Then we are going to continue with a comparative table in which we are going to show you the main characteristics of both, and we will continue with an in-depth explanation of what these characteristics are and what they imply. Finally, we will end up telling you when it is recommended to use HDDs or SSDs, so that if you want to buy one you can make an informed decision.
Hard disk or HDD (Hard Drive Disk)
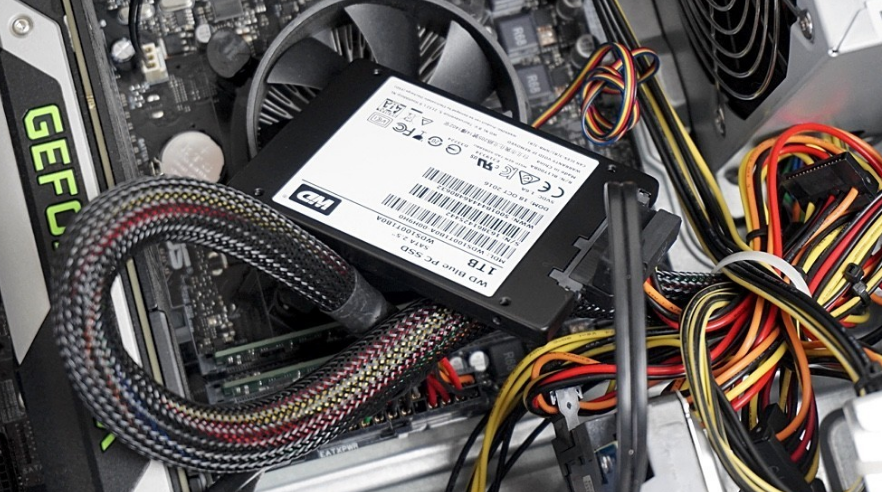
Hard drives, also known as HDDs, are computer components used to permanently store your data. This means that the data is not erased when the unit is turned off, as is the case with data stored in RAM. The first company to market them was IBM in 1956.
They are made up of mechanical parts, hence sometimes called mechanical hard drives, and they use magnetism to record your data and files. It consists of one or several hard disks joined by the same axis that rotates at high speed inside a metallic box. On each platter and each of its faces, a read/write head reads or writes your data to the disks.
The thinner the discs, the better the recording, and the faster they spin, the faster the data is transmitted, both when reading and writing them. Typically, hard drive speeds are 5,400 or 7,200 RPM (revolutions per minute), although some server-based drives can go as high as 15,000 RPM
Regarding the size, the boxes of the mechanical hard drives can be 2.5 “or 3.5”. Its price may vary depending on its size but above all on its storage capacity. The great advantage of these hard drives over SSDs is that they are much cheaper.
Solid state drive or SSD

Solid state drives or SSDs (Solid State Drive) are an alternative to hard drives. The big difference is that while hard drives use moving mechanical components, SSDs store files on microchips with interconnected flash memories. Therefore, we could almost consider them as an evolution of USB memories.
SSDs usually use NAND-based flash memories, which, as they are also non-volatile, keep the information stored when the drive is disconnected. They do not have physical heads to write the data, instead, they include an integrated processor to perform operations related to reading and writing data.
These processors, called controllers, make the “decisions” about how to store, retrieve, cache, and clean data on the drive, and their efficiency is one of the factors that determine the overall speed of the drive. In addition, by not relying on the spinning of a physical component, it also results in a quieter drive than mechanical drives.
In terms of size, these drives are usually 2.5″, and have an almost identical design to mechanical hard drives, which helps them fit into the same casings and slots where conventional hard drives are mounted on a computer. computer.
HDD vs SSD: main differences
| MAIN ADVANTAGES |
SSD |
HDD |
|---|---|---|
|
ABILITY |
Typically between 256 GB and 4 TB |
Typically between 1 and 10TB |
|
CONSUMPTION |
lower consumption |
higher consumption |
|
COST |
much more expensive |
Much cheaper |
|
NOISE |
Quieter due to no moving parts |
Slightly noisier due to moving parts |
|
VIBRATIONS |
Does not vibrate because it has no moving parts |
The rotation of its discs can cause slight vibrations |
|
FRAGMENTATION |
Does not have |
can occur |
|
DURABILITY |
Your cells can be rewritten a limited number of times |
With mechanical parts that can be damaged by movements |
|
OS BOOT TIME |
7 seconds |
16 seconds |
|
DATA TRANSFER |
Typically between 200 and 550 MB/s |
In general between 50 and 150 MB/s |
|
AFFECTED BY MAGNETISM |
No |
Magnetism can delete data |
In this table, you can see the main differences between both storage technologies. The main difference has to do with maximum capacities and price. It must be borne in mind that SSDs are much more modern, so it is normal for their price to be significantly higher. As of today, a 250 GB SSD can be worth the same as a 3 TB HDD.
Being storage units with no moving parts like their predecessors, SSDs have some notable advantages such as lower noise and vibration. It must also be made clear that we cannot say that mechanical hard drives are not extremely noisy either, so it is not a significant difference.
The one that is a notable difference is that speed. In our comparison between the two technologies, we saw how an SSD started an operating system in less than half the time of a 7,200-rpm HDD, and that it more than tripled its data read and write speeds. In our test, we used an HDD that read and wrote data at 150 MB/s and an SSD that read and wrote at 545 MB/s and 525 MB/s.
These specific data for writing and reading data always depend on the different models on the market. But in general, SSD hard drives are always much faster than mechanical ones. Hence precisely its high price.
The great concern around SSDs has always been around their durability, especially because of the few that the first drives to hit the market had. The useful life of solid-state drives directly depends on the amount of data you write to it since each cell in a bank of flash memories can only be written a certain number of times.
A study by Tech Report found that a fairly standard SSD, specifically a Samsung 850 Pro, could last up to 2.4 Petabytes of data written, which is equivalent to 2457.6 Terabytes. Therefore, the duration of one of these disks depends on how long it takes to write and rewrite the hard drive until you reach that amount, which is surely more than the 3 to 5-year warranty that manufacturers usually offer.
One of the drawbacks of SSDs compared to HDDs in terms of durability is that they have a higher failure rate. Even so, this is improving generation by generation and has other advantages such as better resistance to blows. remember, HDDs have mechanical parts, so a hit could cause them to break or wear out sooner, shortening their useful life.
In any case, and to avoid surprises, both in SSDs and in HDDs that can last around 10 years or more, it is best to regularly monitor the health of your hard drive. Here’s a collection of tools you can do it with, so you know when you might be about to experience an error that puts your data at risk.
Which hard drive to choose?
If you usually download a lot of content from the Internet and need large amounts of storage, or if you have a low budget, it is recommended that you continue to use HDDs. They are also a good resource for external hard drives, where storage capacity tends to take precedence over speed.
On the other hand, SSDs are recommended if you want to have a much faster computer. Its speed can make a PC that is a few years old go much faster without having to invest in other components. It is also recommended if you usually work editing multimedia content or are a video game lover since loading processes will speed up thanks to them.
In most cases, however, it is advisable to combine both types of hard drives. In a home tower, for example, you can use an SSD on drive C: to install the operating system there and make everything go faster. You accompany it with an HDD as a secondary disk and you will have a perfect unit in which to store all the heavy files that you have on the computer.
SSD FAQ
1. What does SSD mean?
SSD stands for Solid State Drive, which translated into Spanish means Solid State Drive.
2. What is an SSD hard drive?
SSDs are a new type of storage device that replaces conventional hard drives. They are capable of storing data in a much faster way, which makes the computers that use them much faster.
3. How much does an SSD cost?
SSDs are usually always more expensive than hard drives, and there are several types of them with different price ranges. They also depend on your storage capacity. They can range from 25 euros for a classic 240 GB SSD to 200 euros for a 2 TB PCIe NVMe type.
Sharlene Meriel is an avid gamer with a knack for technology. He has been writing about the latest technologies for the past 5 years. His contribution in technology journalism has been noteworthy. He is also a day trader with interest in the Forex market.









![How to Watch UFC 303 Live Stream Free [Updated 2024] UFC 259 Live Stream Free](https://techsmartest.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/UFC-259-Live-Stream-Free-100x70.jpg)