How does the ping command work and what it is for: because in many circumstances, it is the first diagnostic utility to use.
Often we hear the expressions ping of the connection or ping of the ADSL or ping of the fiber connection.
These terms obviously refer to the latency of the connection (whether it occurs from a fixed location, or whether it is a data connection on a mobile network) or the time that is taken by the data packet to reach the first network device of the Internet provider from which you have taken out a subscription and goes back.
In fact, ping is the diagnostic utility found in all operating systems that measure the packet’s time to reach the indicated destination (a local or remote system) and return to the source (latency).
Gamers speak of low ping when data packets reach an online game server and come back in a short time.
In reality, the connection’s latency should be measured at the first hop or by taking the first network device of the Internet access provider as a reference point or at least the last router crossed before leaving its network.
Measuring the latency using the ping command to different sites, belonging to completely different networks, and hosted on servers located in various places on the planet, will in fact lead to widely differing results.
TIM no longer allows pinging the first hop (192.168.100.1 or 192.168.200.1). For example, trying to type ping 192.168.100.1 or ping 192.168.200.1 at the Windows command prompt will always result in Request timed out.
In the past, this was not the case, and the two hosts responded correctly. Still, today the appearance of the Request expired message is absolutely normal and depends on the configuration made by TIM network technicians.
However, ping values of 80 ms on the first hop are already quite high with a broadband connection (ADSL or, even more so, FTTC / FTTE / FTTH fiber).
For ADSL, the values indicated as minimum acceptable at the contractual level are usually undoubtedly more penalizing. For a 20 Mbps, we speak of 100-120 ms of maximum latency and 0.1% regarding the rate of packet loss.
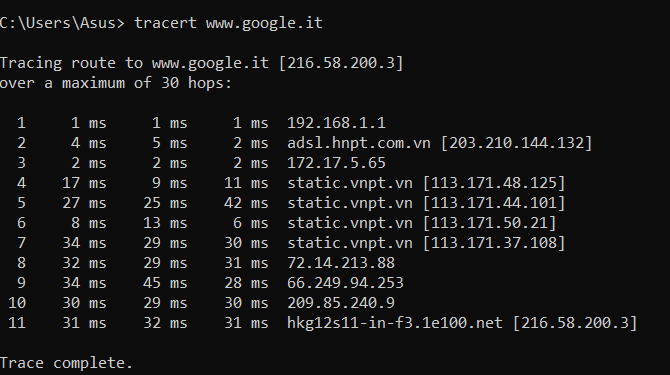
By running the command tracert www.google.com. It is possible to know the path (the “route,” hence the term routing ) that the packets make to reach their destination.
Starting from the figure’s example, launching the ping command 195.22.192.72 will query the first hop that is encountered outside the TIM network, obtaining a reliable ping value (all network devices belonging to the TIM network are no longer “pingable”).
Beyond this hop, latency values usually increase depending on the networks crossed and the state of the links (presence of congestion).
The tests should always be performed when there are no data transfers in progress and from devices connected to the local network. Otherwise, the latency value will inevitably be distorted.
How to PING at the Windows Command Prompt?
To start a ping from the Windows Command Prompt, press the Windows + R key combination, type cmd, and hit the Enter key.
At this point, by typing ping followed by an IP address or a domain name in mnemonic format (example: www.google.com), four test data packets (ICMP) of 32 bytes each will be sent, and the latency in milliseconds will be calculated ( ms).
By issuing the ping -t www.google.com command, the system in use will continue to send ICMP packets indicating the response times.
A sudden increase in times is synonymous with temporary network congestion; if, however, the latency was also high on the first hop-out of the telecommunications operator’s network, in all probability, some local device (even one is enough) is completed using the available bandwidth for upload and/or download.
The ping -t command is also useful in particular scenarios to check when the Internet connection is actually available: Internet connection on the train.
Check if it was possible to reach a website and how quickly you receive a response.
The ping utility allows you to check if you got a response from any specified website using its mnemonic address. Example: ping www.google.com.
However, it is important to keep in mind that not all remote servers respond to ping (including those that deliver websites): they can respond or not respond depending on the firewall or operating system settings.
By accessing your modem router’s administration panel, it is still a good idea to check that the device does not respond to ICMP requests (ping) on the public IP address. You can look for the setting Respond to ping on the Internet port, Respond to ICMP requests, or similar.
Check if the DNS server is working.
If, by launching the ping command, www.google.it or, in any case, ping followed by the mnemonic address of the website to be checked, you get the messages “request expired,” “unable to find the host,” or “general error,” it is good to try to write ping 8.8.8.8.
If you get an answer, it means that the DNS servers set up locally are most likely not working correctly and won’t allow you to resolve domain names.
It will therefore be necessary to check its configuration. In Windows, it is done by pressing the key combination Windows + R, then typing ncpa.cpl, and finally clicking with the right button on the network interface in use (choose Properties then check the Internet Protocol version 4 and Internet Protocol version 6 settings ).
Obtain the IP address corresponding to a domain name
Although the most suitable utility to obtain the list of IP addresses associated with a domain name is nslookup, by typing ping followed by a domain name, you can immediately know the corresponding IP address public.
Check if you get sheltered from the router and other devices connected to the local network.
The Ping utility is a great way to check if you are getting a response from your local network’s devices. The ping command can be followed by a private IP or by a name (e.g., MY-NAS, PC-USER, and so on).
The excellent free Fing application allows you to search for all devices connected to the local network, discover the activated services, and start the ping command.
It should be noted that if the network connection on a Windows system is set to Public Network, the device – by default – will never respond to ping requests: see Difference Between Public Network and Private Network in Windows 10.
Launch the ping command on the loopback address
The loopback address (127.0.0.1) corresponds to the local network interface: typing ping 127.0.0.1 can verify that everything is working correctly.
If you receive the General Error message when issuing this command, you will need to recheck the network interface settings at the operating system level.
If this is not possible, in particular, “reset” the network connection as explained in point ” Reset the network connection “.
What is Freshping, and how does it work?
Among the many online services that allow you to launch the Ping command from remote servers, therefore placed outside your network, we also mention the excellent Freshping.
In reality, Freshping does not send simple ICMP requests as is normally done with the Ping command but tries the connection to the website specified in the appropriate box.

The advantage of Freshping is that it can respond to the actual reachability of any website even if the server in question was set not to respond to ping and more generally to all ICMP requests.
A tech-savvy writer with a knack for finding the latest technology in the market, this is what describes John Carter. With more than 8 years of experience as a journalist, John graduated as an engineer and ventured soon into the world of online journalism. His interest includes gadget reviews, decoding OS errors, hunting information on the latest technology, and so on.