
We are going to explain to you what are the differences between the different types of USB standards and connectors. Surely you have already noticed that your current smartphone does not have the same USB port as those of a few years ago, especially if you already have one that is reversible or type C. But all that jargon of types A, B, and C, as well as Minis or Micros, can be a bit confusing, which is why we will try to explain it in the simplest way possible.
In short, USB standards are evolving over the years in the same way as other technological components, and that is why from time to time, a new standard comes out faster than its predecessor. The ports are also evolving; different USB standards can use some connectors.
Types of USB standards
Let’s start by discussing the different types or versions of USB standards, which are classified into four types depending on the speed at which they transfer your data. Before its official launch in 1996, USB had some previous versions such as USB 0.7 and 0.8 from 1994, 0.9 from 1995, and 0.00 from August 1996, but we will start from version 1.0, although taking into account that They are already so old that they are difficult to find.
- USB 1.0: They are the oldest and the lowest speed USB standard. Its transfer rate is up to 1.5 Mbit/s (188 kB/s), and it is mainly used in human interfaces such as keyboards, mice, or webcams.
- USB 1.1: It is the improvement of 1.0, known as full speed or “plug and play”. Its transfer rate goes up to 12 Mbit/s (1.5 MB/s), although it was still far from the speeds the following standards would achieve.
- USB 2.0: Also known as high-speed, it reaches transfer rates of up to 480 Mbit/s (60 MB/s), although, in practice, it usually stays at 280 Mbit/s (35 MB/s). It is the most widespread standard currently, with two lines for data and two for high-speed power. You can also charge devices at 2.5W of power.
- USB 3.0: Also called Super High Speed, it has a transfer rate of up to 4.8 Gbit/s (600 MB/s), ten times the speed of USB 2.0, thanks to its five extra contacts.
- USB 3.1: Super High Speed+ or SuperSpeed is twice its predecessor’s speed, with a transfer rate of up to 10 Gbit/s (1.25 GB/s). It is the one that is usually used by Type C connectors. We will explain a little later.
- USB 3.2: Introduced in February 2019. It can offer transfer rates of up to 20 Gbit/s (2.5 GB/s), and the first peripherals to use it arrived in 2020.
- USB 4.0 – Also introduced in 2019, it is the most recent standard. USB4 will be able to offer transfer rates of up to 40 Gbit/s (5 GB / s), and the first computers to use it have arrived in 2021.
Types of USB connectors
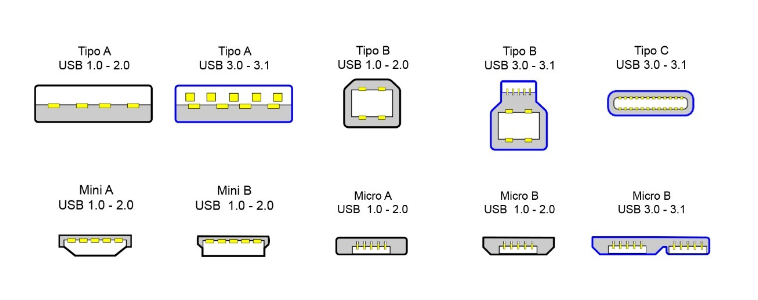
As you can see, standards are one thing, but the types of connectors used by USB are pretty different. Next, we will tell you what the main types are and their main characteristics, including the standards that each one of them usually has.
- USB Type A: It has been the predominant connector between peripherals and main computers until the arrival of smaller ones. USB Type A can be used with USB 1.0, 2.0 standards and USB 3.0 and 3.1. However, the connectors that use the 3.0 standard differ from the rest by having an internal tab, like a small blue plastic. Therefore, if it does not have it, it is because it is of lower speeds.
- USB Type B is the connector typically used to connect to peripherals such as printers and scanners, though often just to provide power. There are two types of Type B connectors, the “conventional” one for USB 1.0 and 2.0 standards and one with a slightly different shape and a blue tab on the inside for USB 3.0.
- USB Type C: It is the most modern type of connector and is the successor to MicroUSB. It is characterized by being completely reversible, so you can always connect it on either side. These are also the connectors used by Thunderbolt 3, an alternative standard to HDMI.
- Mini USB: The first type of USB was reduced in size to connect smaller peripherals. It was widely used by cameras and mobile phones, especially in the Mini B model, but that was many years ago.
- Micro USB: Successor to Mini USB, it has been very popular and the most used for small devices. Possibly, if your mobile is of a lower range or is a couple of years old, you will still find it, although it has also been used in many other peripherals.
Sharlene Meriel is an avid gamer with a knack for technology. He has been writing about the latest technologies for the past 5 years. His contribution in technology journalism has been noteworthy. He is also a day trader with interest in the Forex market.










