How to disable UPnP and why to do it? Akamai raises the alarm: 4.8 million routers expose UPnP functionality on the WAN port.
All modern routers and modem routers offer support for UPnP ( Universal Plug and Play ), a protocol designed to simplify the connection between remote devices and hosts.
UPnP allows us to set up a peer-to-peer network between devices of all kinds and is based on an open and distributed architecture built using the Internet network protocols IP, TCP, UDP (port 1900), and HTTP.
The UPnP functionality on the router has an undeniable advantage: it allows you to open the incoming ports for those programs installed on devices connected to the local network via Ethernet cable or WiFi, allowing connection requests from remote users.
UPnP then allows you to open ports on your router to server functionality programs instantly. Otherwise, with UPnP disabled, to achieve the same result, you should access the router administration panel, open the incoming ports, and activate the so-called port forwarding.
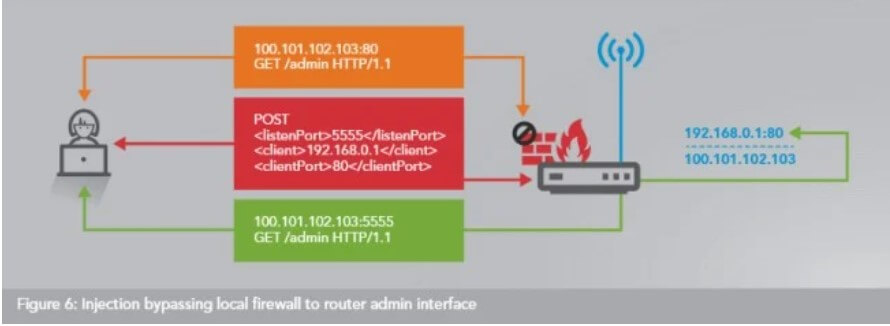
UPnP can represent a significant security problem. Allowing an application running on a workstation or device connected to the local network to open incoming TCP or UDP ports on your router automatically is a reckless action.
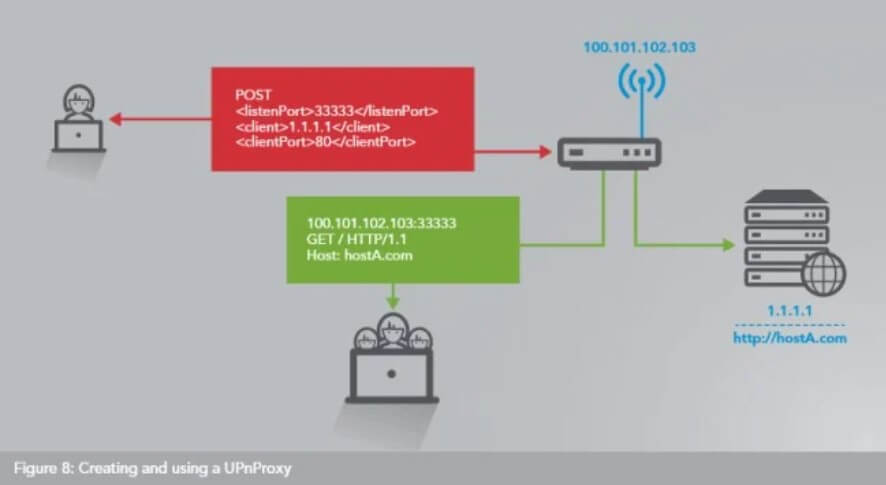
For this reason, without any reservations, we recommend that you disable UPnP.
To do so, you must bring in the router’s configuration panel, enter the section UPnP and uncheck Enable UPnP (also check the doors open and submit the appropriate section, for example, Port Forwarding, Port Forwarding, or Forwarding/door activation ).
The pressing need for disabling UPnP is confirmed today, once again, by Akamai, who published a study on the protocol and the UPnProxy vulnerability.
Akamai found that not only do most routers use UPnP but that approximately 4.8 million routers expose UPnP functionality over the WAN port, making it possible for device administration even to unauthorized remote users.
In other words, a third party can configure the router as it sees fit, using it in some cases as a proxy to other shores. By doing so, a cybercriminal can mask his malicious activities and present himself to remote servers with others’ public IP (making the responsibility for an attack fall on unwitting users).
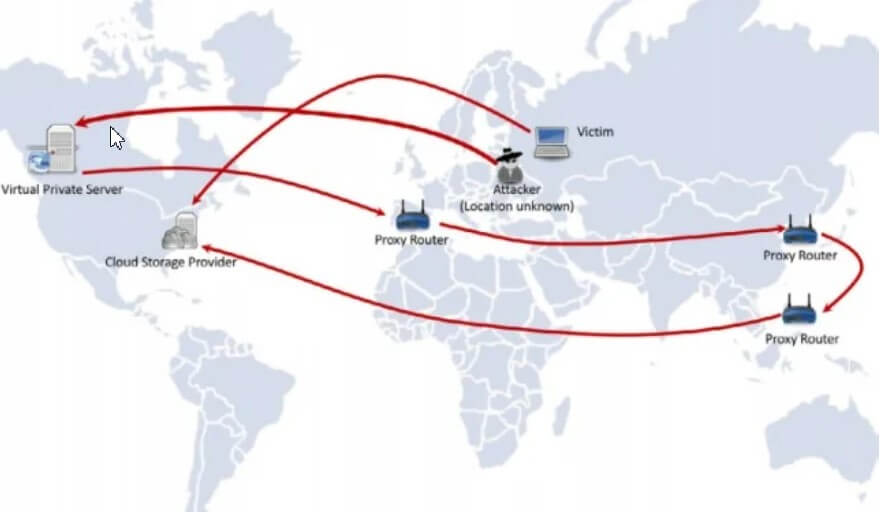
The UPnProxy vulnerability, as Akamai analysts dubbed it, allows a remote attacker to exploit routers that support UPnP and expose the functionality on the WAN port to bypass firewalls and connect with private IPs internal to the local network or to redirect connection requests to completely different IP addresses or domain names.
UPnP can, in fact, also be exploited to modify the routing tables and force the routing of connection requests of users connected to the LAN to websites other than those they intend to visit, with all the harmful consequences that arise.
Akamai has compiled a list of routers and modem routers that expose UPnP on the WAN port to help users.
There are 400 vulnerable devices made by 73 different manufacturers: they could be exposed to UPnProxy attacks in some cases.
To find out the list of routers affected by the problem, we suggest you download this document in PDF format and go to pages 15, 16, and 17.
To prevent UPnProxy attacks, the manufacturer’s release – of an updated firmware is required to correct UPnP configurations and adequately protect the device and systems connected to it. And if the firmware is not available, it is better to set aside the router indicated as vulnerable.
Akamai (see page 13 of the aforementioned document) has also published a script that allows you to identify vulnerable routers or those already exploited in UPnProxy attacks.
The script must be run by connecting to the router via SSH: it is usually necessary to activate this feature from the router configuration panel, in the section dedicated to more experienced users, and connect via Telnet or PuTTY.
To learn more, see also the article Port scanner: scan all ports on the public IP.
A tech-savvy writer with a knack for finding the latest technology in the market, this is what describes John Carter. With more than 8 years of experience as a journalist, John graduated as an engineer and ventured soon into the world of online journalism. His interest includes gadget reviews, decoding OS errors, hunting information on the latest technology, and so on.













